At articleosti4504821 title calibration of a whole body radioactivity counter for the measurement of body potassium content in clinical studies author hughes d and williams r e abstractnote doi journal clin. In health physics whole body counting refers to the measurement of radioactivity within the human body.
Uses Of Radiation Questions
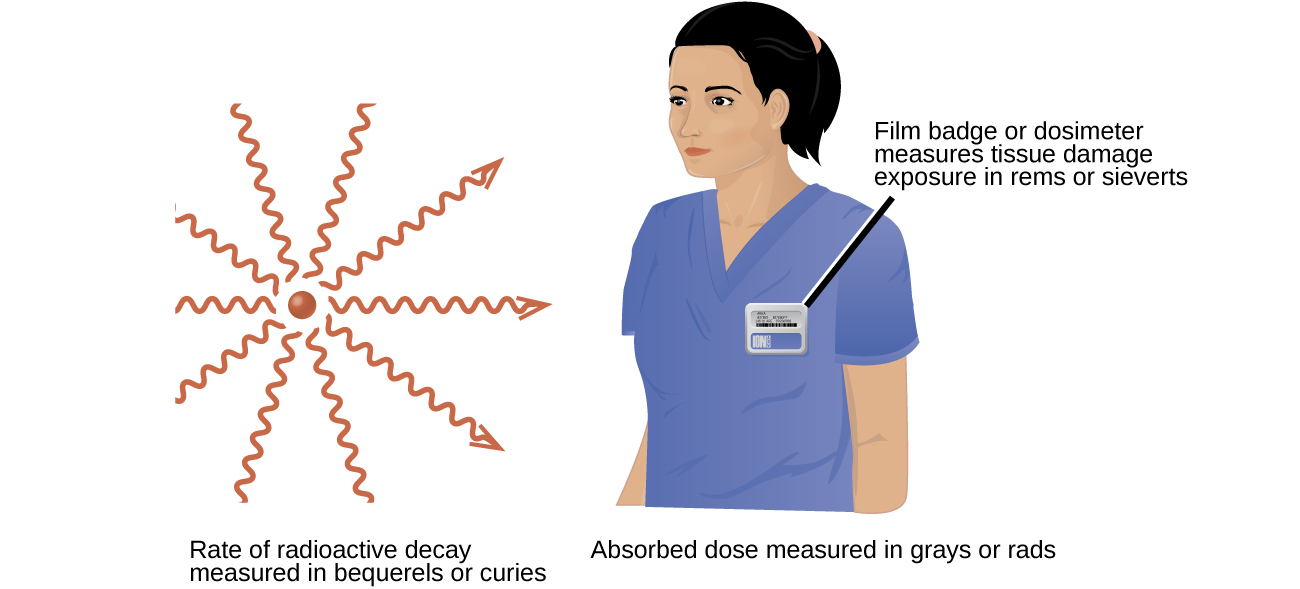
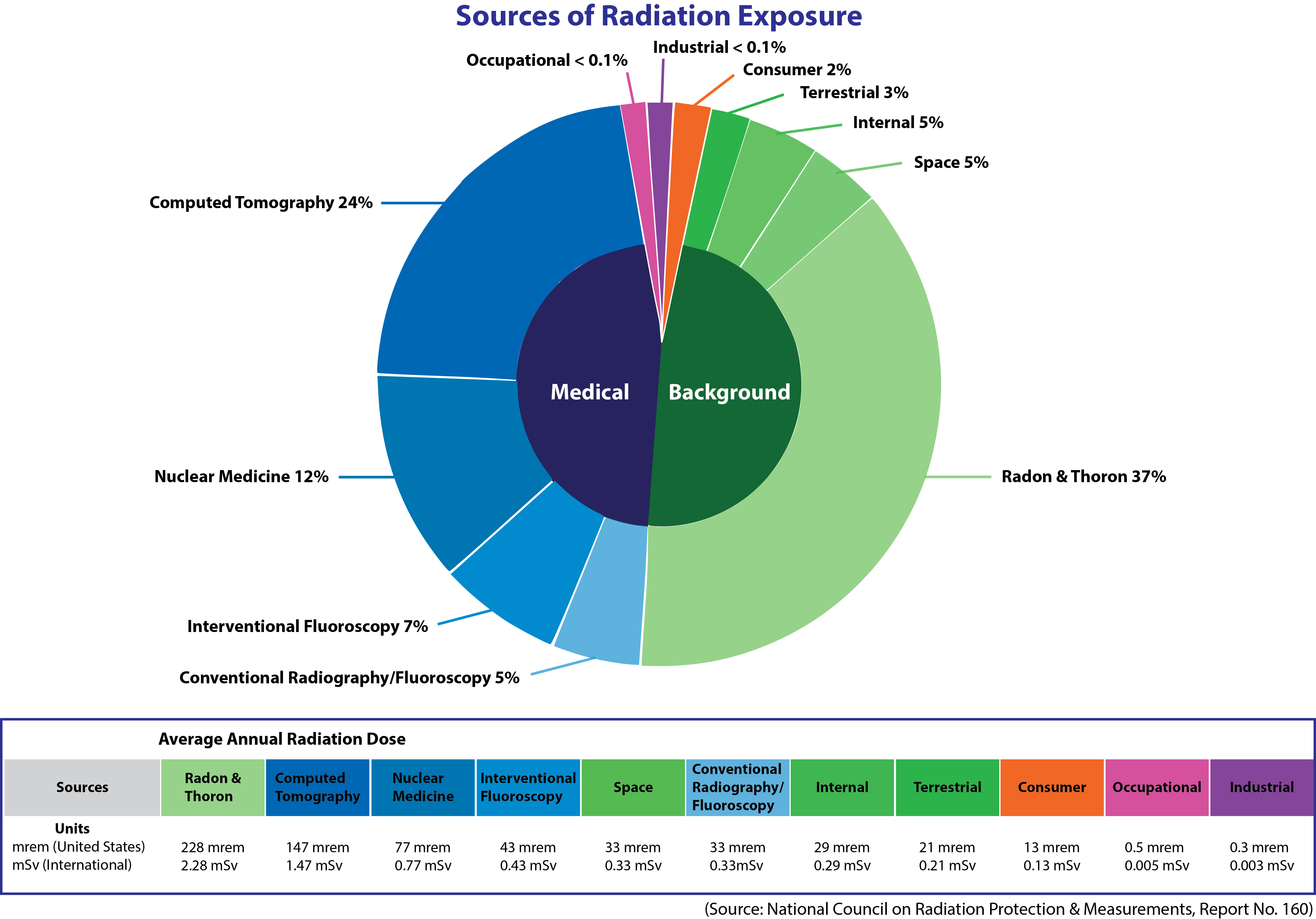
Body radioactivity measurement. Radiation can be measured using sensitive detectors in a whole body counter. Some geiger counters and other detection devices can measure dose or the amount of radiation a body or object absorbs. The difference between the rad and rem is that the rad is a measurement of the radiation absorbed by the material or tissue. Identify radiation dose with a device that measures grays or sieverts. 495 502june 1967 number volume place country unknowncode not available year sun jan 01 000000 est 1967 month sun jan 01. Units for dose equivalent are the roentgen equivalent man rem and sievert sv and biological dose equivalents are commonly measured in 11000th of a rem known as a millirem or mrem.
These dosimeters cannot measure exposure received from low level energy beta emitters like h 3 c 14 s 35 or ni 63. By contrast the dose equivalent is larger than the absorbed dose for alpha and neutron radiation because these types of radiation are more damaging to the human body. The rem is a measurement of the biological effect of that absorbed radiation. All tld dosimeters whole body ring or area dosimeters are limited to measuring high energy beta radiation and gammax ray exposure. In the us the unit for this measurement is called the radiation absorbed dose rad. Electronic dosimeters are also used for direct reading of dose.
A radioactive atom gives off or emits radioactivity because the nucleus has too many particles too much energy or too much mass to be stable. Absorbed dose is a dose quantity which is the measure of the energy deposited in matter by ionizing radiation per unit mass. These detectors can measure the gamma rays emitted by radioactive materials that are in or on the body. It is also used to directly compare the effect of radiation. In certain circumstances beta emitters can be measured but with degraded sensitivity. The sievert is important in dosimetry and radiation protection and is named after rolf maximilian sievert a swedish medical physicist renowned for work on radiation dose measurement and.
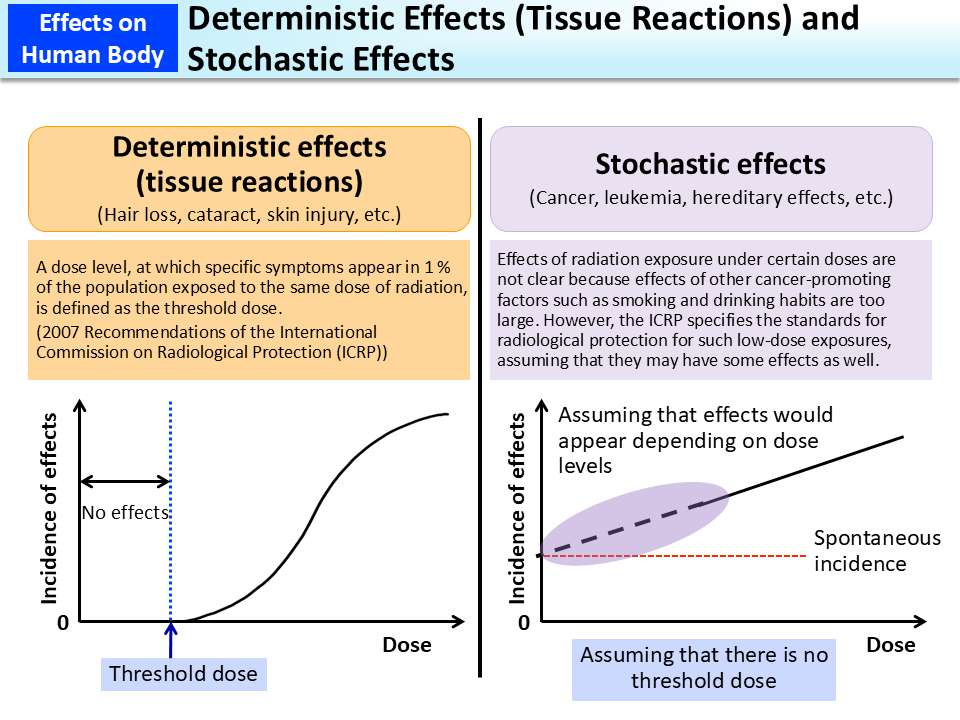
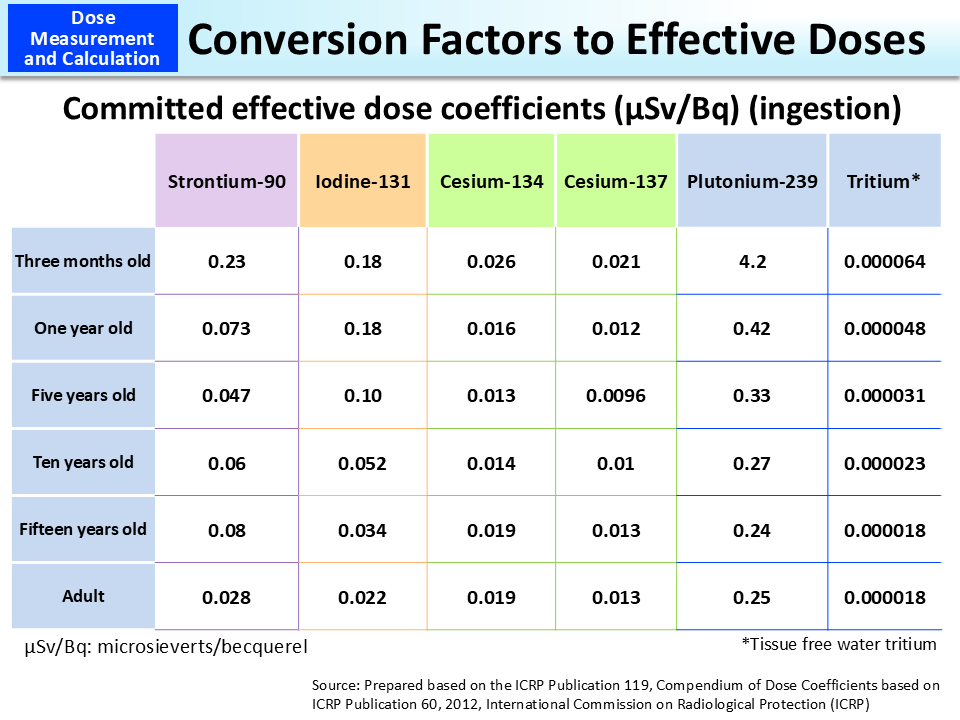
Different radioactive materials will give off gamma rays of different energies which is one technique to identify the material. Quality factor q beta gamma and x rays 1 thermal neutrons 3 fast n a and protons 10 heavy and recoil nuclei 20. Alpha particle decays can also be detected indirectly by their coincident gamma radiation. Sv is a derived unit of ionizing radiation dose in the international system of units si and is a measure of the health effect of low levels of ionizing radiation on the human body. When the amount of radiation being emitted or given off is discussed the unit of measure used is the conventional unit ci or the si unit bq. Absorbed dose is used in the calculation of dose uptake in living tissue in both radiation protection reduction of harmful effects and radiology potential beneficial effects for example in cancer treatment.
The technique is primarily applicable to radioactive material that emits gamma rays.