And the relationship between measurable concentrations of the drug in serum and other bodily fluids and concentrations in tissue remain. The concentrations of the respective drugs in simultaneously collected samples of fluid from each diffusion chamber were measured and compared with concentrations found at the same time in serum.
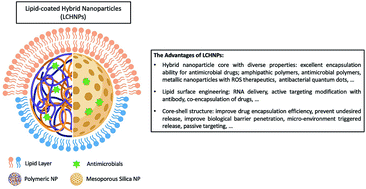
Therapeutic Lipid Coated Hybrid Nanoparticles Against
Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids. In human subjects concentrations of drug in body fluids have been reported 4 7 9 11 12. Serum or edta treated plasma is. Laboratory tests used to guide antimicrobial therapy. We are losing the war against bacteria. Serum protein binding determines the level of free drug available to diffuse across membranes 1 16 18 22. With the availability of rapid accurate assays the measurement of antibiotic material in serum and other body fluids is feasible desirable and widely practiced for these purposes.
Soluble agents penetrate to a greater extent 16. Humanserum pools are prepared. For the other body fluids listed the subjects were generally hospitalized patients table 2. Human serum samples containing unknown con centrations ofan antimicrobial are assayed as above but a normal human serum pool is used as diluent. Occasionally aminoglycoside concentrations have been measured in other body fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid csf to assess the degree of antibiotic penetration into the space or to assure adequate intrathecal dosing. All chambers were tolerated well and the method proved to be effective for collecting data on the distribution of drugs throughout the body.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy june 1993 p. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids biological assys immunoassays chromatographic assays. A major factor influencing penetration is the scrum protein binding of the antimicrobial drug. Antimicrobial levels and renal function for most antimicrobial agents renal excretion is the major pathway for elimination from the. All serum results are referred to standard curves established with serumdiluents. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids.
The reference standard concentration is also pre pared in a normal human serum pool. In contrast dilution methods allow determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration of an agent which can be correlated with blood urine and other body fluid levels of the antimicrobial agent. The values given for serum and urine were obtained from normal adults in controlled phar macologic studies table 1. The body site from which the organism was isolated. Laboratory tests that can be helpful in guiding antimicrobial therapy include antimicrobial susceptibility testing determination of bacterial beta lactamase production assay of serum inhibitory and bactericidal activity and assay of specific antibiotic levels in serum. Accurate measurement of serum concentrations of antimicrobial agents is important when the margin between therapeutic and toxic levels is narrow.
The measurement of antibiotic concentrations in various fluids has been a prominent aspect of the evaluation of new antibiotics and the quality control of their manufacture.